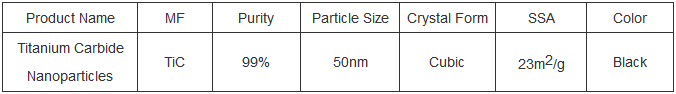
In the ruthless landscapes of modern-day market– where temperatures soar like a rocket’s plume, stress squash like the deep sea, and chemicals corrode with relentless force– products have to be greater than long lasting. They need to prosper. Get In Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics, a marvel of engineering that turns extreme problems right into chances. Unlike regular porcelains, this material is born from an one-of-a-kind procedure that crafts it right into a lattice of near-perfect crystals, endowing it with stamina that equals metals and strength that outlasts them. From the fiery heart of spacecraft to the sterilized cleanrooms of chip manufacturing facilities, Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics is the unsung hero enabling innovations that press the boundaries of what’s possible. This write-up dives into its atomic keys, the art of its creation, and the strong frontiers it’s dominating today.
The Atomic Plan of Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics
(Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics)
To grasp why Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics differs, envision building a wall not with bricks, however with microscopic crystals that secure with each other like puzzle items. At its core, this product is made from silicon and carbon atoms set up in a duplicating tetrahedral pattern– each silicon atom adhered firmly to four carbon atoms, and vice versa. This framework, comparable to ruby’s but with alternating components, develops bonds so solid they stand up to breaking even under enormous anxiety. What makes Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics special is exactly how these atoms are organized: during production, little silicon carbide bits are heated to extreme temperatures, creating them to dissolve slightly and recrystallize right into bigger, interlocked grains. This “recrystallization” procedure removes weak points, leaving a product with an attire, defect-free microstructure that behaves like a single, huge crystal.
This atomic consistency gives Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics three superpowers. First, its melting factor exceeds 2700 levels Celsius, making it one of the most heat-resistant products recognized– ideal for settings where steel would vaporize. Second, it’s exceptionally solid yet lightweight; an item the dimension of a brick considers less than fifty percent as long as steel however can birth lots that would certainly crush aluminum. Third, it disregards chemical assaults: acids, antacid, and molten metals move off its surface area without leaving a mark, thanks to its steady atomic bonds. Think about it as a ceramic knight in beaming armor, armored not simply with firmness, however with atomic-level unity.
But the magic does not quit there. Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics additionally performs heat remarkably well– virtually as efficiently as copper– while remaining an electrical insulator. This rare combination makes it important in electronic devices, where it can blend heat away from sensitive parts without running the risk of brief circuits. Its low thermal growth implies it hardly swells when heated up, preventing fractures in applications with fast temperature level swings. All these characteristics stem from that recrystallized framework, a testament to how atomic order can redefine material potential.
From Powder to Efficiency Crafting Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics
Creating Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics is a dancing of precision and patience, turning simple powder right into a product that opposes extremes. The journey begins with high-purity basic materials: fine silicon carbide powder, usually combined with percentages of sintering help like boron or carbon to aid the crystals expand. These powders are initial shaped into a harsh kind– like a block or tube– making use of approaches like slip casting (pouring a fluid slurry right into a mold) or extrusion (compeling the powder with a die). This initial form is simply a skeletal system; the genuine change occurs next.
The key step is recrystallization, a high-temperature ritual that reshapes the material at the atomic degree. The shaped powder is put in a heating system and warmed to temperature levels between 2200 and 2400 levels Celsius– hot sufficient to soften the silicon carbide without thawing it. At this stage, the small particles begin to dissolve slightly at their edges, allowing atoms to migrate and reorganize. Over hours (or even days), these atoms locate their excellent placements, merging into larger, interlacing crystals. The outcome? A thick, monolithic framework where previous bit borders disappear, changed by a seamless network of stamina.
Controlling this process is an art. Too little heat, and the crystals do not expand big enough, leaving weak points. Too much, and the material may warp or create fractures. Experienced technicians keep track of temperature level contours like a conductor leading a band, changing gas circulations and home heating prices to lead the recrystallization completely. After cooling, the ceramic is machined to its last measurements utilizing diamond-tipped tools– given that also set steel would certainly struggle to suffice. Every cut is slow and deliberate, protecting the material’s integrity. The final product is a component that looks straightforward however holds the memory of a journey from powder to perfection.
Quality assurance guarantees no defects slip via. Engineers examination samples for thickness (to verify complete recrystallization), flexural stamina (to measure bending resistance), and thermal shock resistance (by plunging hot items right into cool water). Just those that pass these tests gain the title of Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics, all set to face the world’s toughest tasks.
Where Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics Conquer Harsh Realms
The true examination of Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics lies in its applications– locations where failing is not an option. In aerospace, it’s the foundation of rocket nozzles and thermal protection systems. When a rocket launch, its nozzle endures temperature levels hotter than the sun’s surface and pressures that squeeze like a gigantic fist. Steels would thaw or warp, however Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics stays stiff, directing thrust successfully while withstanding ablation (the steady erosion from hot gases). Some spacecraft also utilize it for nose cones, securing delicate instruments from reentry heat.
( Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics)
Semiconductor manufacturing is one more arena where Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics radiates. To make integrated circuits, silicon wafers are heated in heating systems to over 1000 degrees Celsius for hours. Conventional ceramic carriers might pollute the wafers with impurities, but Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics is chemically pure and non-reactive. Its high thermal conductivity also spreads warm uniformly, protecting against hotspots that could ruin fragile circuitry. For chipmakers going after smaller, much faster transistors, this product is a quiet guardian of pureness and accuracy.
In the energy field, Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics is revolutionizing solar and nuclear power. Solar panel suppliers utilize it to make crucibles that hold molten silicon throughout ingot production– its heat resistance and chemical security prevent contamination of the silicon, improving panel efficiency. In nuclear reactors, it lines parts exposed to radioactive coolant, withstanding radiation damage that deteriorates steel. Also in combination research, where plasma gets to numerous levels, Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics is tested as a potential first-wall material, entrusted with including the star-like fire securely.
Metallurgy and glassmaking additionally rely upon its toughness. In steel mills, it forms saggers– containers that hold liquified metal throughout heat treatment– standing up to both the steel’s warm and its corrosive slag. Glass manufacturers utilize it for stirrers and mold and mildews, as it won’t react with liquified glass or leave marks on finished products. In each situation, Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics isn’t just a component; it’s a companion that enables processes once assumed also severe for porcelains.
Innovating Tomorrow with Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics
As modern technology races ahead, Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics is advancing as well, finding brand-new roles in arising areas. One frontier is electric lorries, where battery loads generate extreme warm. Engineers are evaluating it as a warmth spreader in battery modules, pulling warmth away from cells to prevent getting too hot and prolong array. Its lightweight additionally helps keep EVs effective, a critical factor in the race to replace gas cars.
Nanotechnology is an additional location of growth. By mixing Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics powder with nanoscale ingredients, researchers are producing compounds that are both more powerful and much more flexible. Visualize a ceramic that flexes slightly without breaking– valuable for wearable tech or adaptable solar panels. Early experiments reveal assurance, meaning a future where this product adapts to new shapes and stress and anxieties.
3D printing is likewise opening up doors. While traditional methods limit Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics to simple shapes, additive production permits complicated geometries– like latticework frameworks for light-weight warm exchangers or customized nozzles for specialized commercial procedures. Though still in advancement, 3D-printed Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics might quickly enable bespoke parts for particular niche applications, from clinical gadgets to room probes.
Sustainability is driving advancement also. Manufacturers are discovering means to decrease energy usage in the recrystallization procedure, such as utilizing microwave heating as opposed to standard heaters. Reusing programs are also arising, recouping silicon carbide from old parts to make brand-new ones. As industries focus on environment-friendly methods, Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics is confirming it can be both high-performance and eco-conscious.
( Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics)
In the grand story of materials, Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics is a phase of strength and reinvention. Born from atomic order, shaped by human ingenuity, and checked in the toughest corners of the globe, it has come to be important to industries that risk to fantasize big. From launching rockets to powering chips, from subjugating solar energy to cooling down batteries, this material does not simply make it through extremes– it grows in them. For any type of firm intending to lead in innovative production, understanding and utilizing Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics is not just a choice; it’s a ticket to the future of performance.
TRUNNANO chief executive officer Roger Luo stated:” Recrystallised Silicon Carbide Ceramics excels in extreme industries today, resolving harsh challenges, broadening into future tech technologies.”
Distributor
RBOSCHCO is a trusted global chemical material supplier & manufacturer with over 12 years experience in providing super high-quality chemicals and Nanomaterials. The company export to many countries, such as USA, Canada, Europe, UAE, South Africa, Tanzania, Kenya, Egypt, Nigeria, Cameroon, Uganda, Turkey, Mexico, Azerbaijan, Belgium, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Brazil, Chile, Argentina, Dubai, Japan, Korea, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, Australia,Germany, France, Italy, Portugal etc. As a leading nanotechnology development manufacturer, RBOSCHCO dominates the market. Our professional work team provides perfect solutions to help improve the efficiency of various industries, create value, and easily cope with various challenges. If you are looking for ceramic bearing, please feel free to contact us and send an inquiry.
Tags: Recrystallised Silicon Carbide , RSiC, silicon carbide, Silicon Carbide Ceramics
All articles and pictures are from the Internet. If there are any copyright issues, please contact us in time to delete.
Inquiry us